The work presented in this dissertation deals mainly with
the interaction of extragalactic jets from powerful double radio
sources and their environment. In Chapter II the
hydrodynamics needed for all the calculations used later are described.
This is achieved by converting the basic equations of relativistic
hydrodynamics into useful forms for the study of jet interactions,
without considerations of magnetic fields. Chapter III
deals with the problem of bending of jets due to jet-cloud interactions.
Chapter IV analyses the stability of curved jets against
the formation of internal shocks. Chapter V
deals with the problem of the collision between a shock wave and a
high density region, or cloud. Finally, in Chapter VI the
astrophysical implications of all the calculations presented in this
dissertation are discussed.
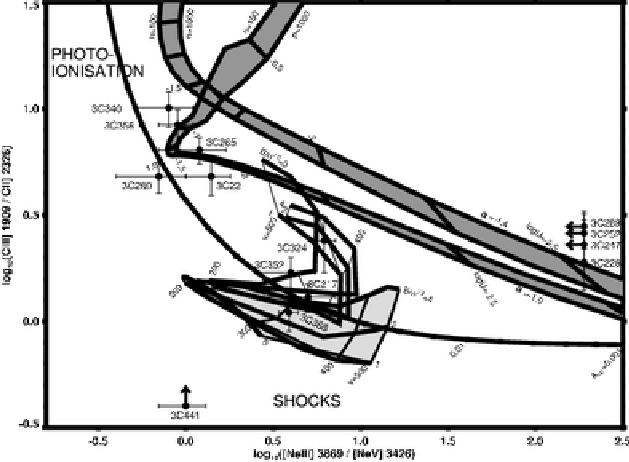
Figure I.9:
Emission line diagnostic
plot for a particular sample of 3CR radio galaxies,
compared with theoretical predictions (Best et al., 2000).
Some of these galaxies present the alignment effect shown
in figs.(I.8)-(I.9). The upper shadowed
regions are simple photoionisation models. The continuous curve
that increases towards the right of the diagram is the model
for photoionisation models including matter bounded clouds, that
is, photoionisation of a composite population containing both
optically thin (matter bounded) and optically thick (ionisation
bounded) clouds. The lower shadowed region is predicted by
shock ionisation models. The upper unshadowed region above
this last one is the one for shock models including a precursor
region, that is an upstream ionised region produced by photons
diffusing into this preshocked gas. The five galaxies plotted
at the right of the diagram have no data available for one of
their emission lines.
|
|
Sergio Mendoza Fri Apr 20, 2001